Careers
Join us to grow your skills, unlock your potential, and discover career paths you never imagined, all while keeping Singapore safe and secure.
On this page
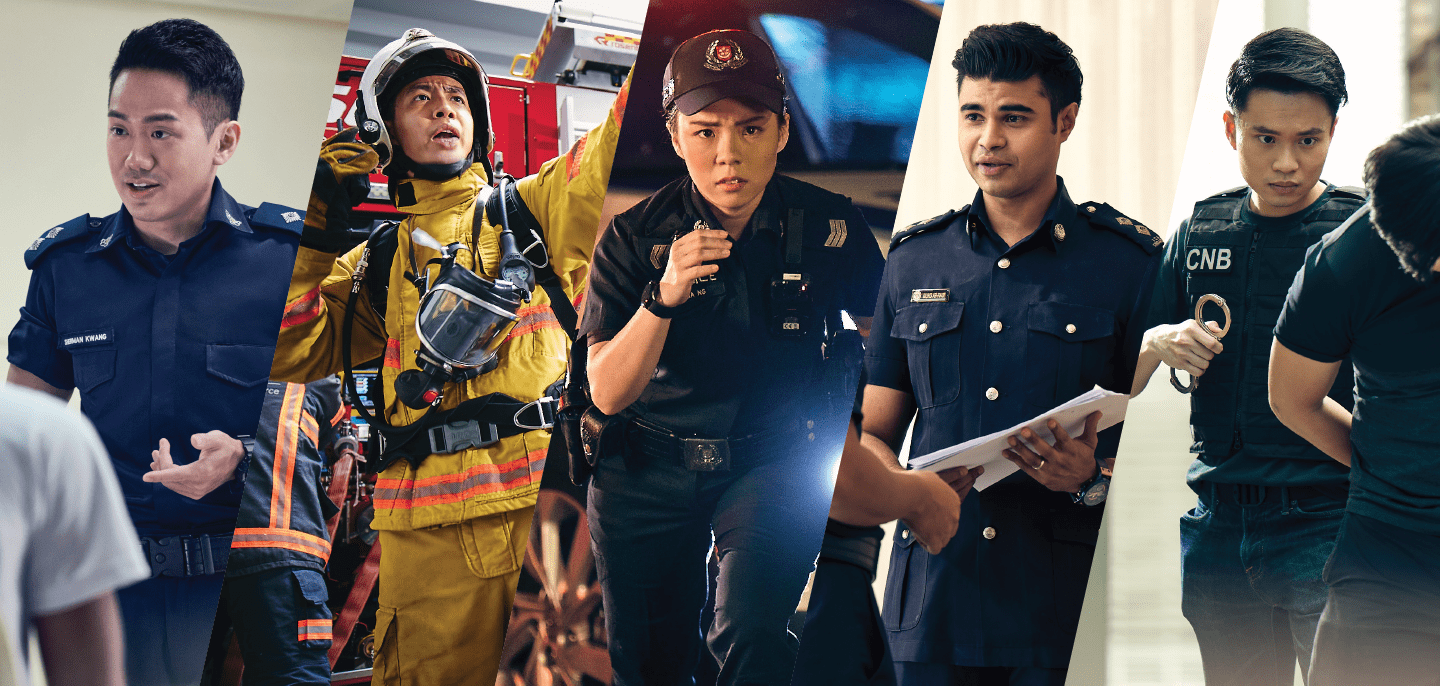

Where safeguarding our home grows you in unexpected ways
Grow beyond what you thought possible
Pick up new skills, tackle fresh challenges, and surprise yourself with what you can achieve. You'll find yourself growing beyond what you thought possible, in ways only a career with us can offer.
Safeguard the place we call home
The Home Team's mission touches everyone, every day. Whether you are in a uniformed or a civilian career with us, you will directly impact lives, safeguarding your loved ones and our Home.
Where you genuinely matter
Be part of a place where colleagues become lifelong friends, leaders genuinely care about your growth, and everyone supports each other. Your wellbeing matters as much as the mission.
Build tomorrow's safety, today
Step into a culture where we're always finding better ways to keep Singapore safe. From fresh approaches to everyday challenges to creative problem-solving, we constantly innovate - your ideas matter.
Career Tracks
Where do you see yourself? Explore our uniformed and civilian careers.
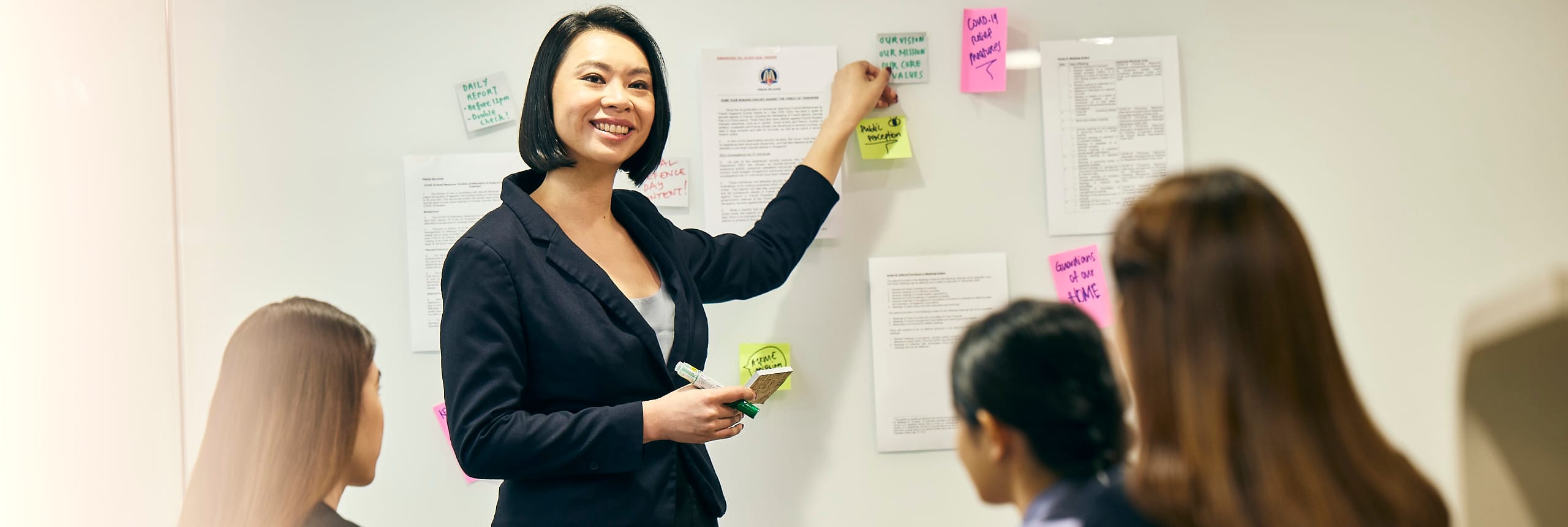

Civilian (Generalist) Careers
Generalist career offering exposure to various domains of work (e.g. Policy, International Relations, HR, Communications), and across agencies in the Home Team.
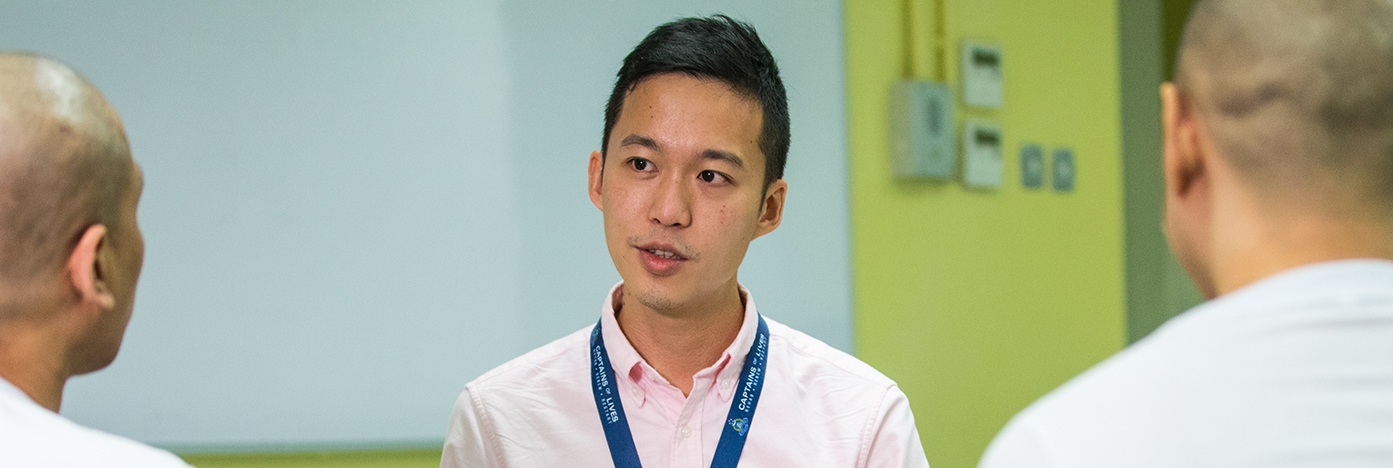

Civilian (Specialist) Careers
Home Team Specialist roles in Intelligence, Commercial Affairs and Psychology.
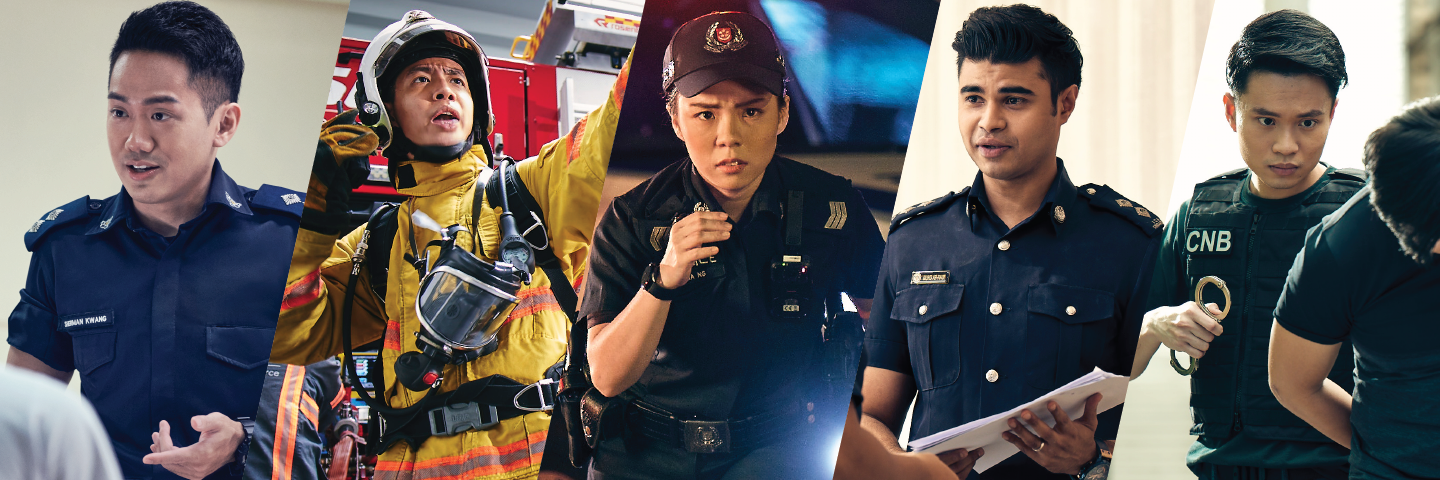

Uniformed Careers
Frontline uniformed careers with the Singapore Police Force, Singapore Civil Defence Force, Immigration & Checkpoints Authority, Singapore Prison Service and Central Narcotics Bureau.

Other Civilian Schemes
Other civilian career schemes are available in the Home Team with the Internal Security Department, HTX (Home Team Science and Technology Agency), Yellow Ribbon Singapore, Gambling Regulatory Authority and Home Team Academy.
For Students
Grow beyond expectation with us. Find out more about the scholarships and internships, in both uniformed and civilian career tracks, which are available in the Home Team.

MHA Internship
Gain experience and get the opportunity to make an impact in the Home Team agency of your choice.

MHA Scholarships
Find out about our Home Team scholarships for outstanding undergraduates and start your leadership journey with us.
Updates & Events
Check out MHA's LinkedIn page for latest career, internship and scholarship updates and events.
We're Hiring
At MHA, you have many ways to make a difference. Check out our current job openings and apply via Careers@Gov.
Life in the Home Team
Get to know our people and find out about different careers in the Home Team




